SILAC-based Quantitative Phosphoproteome Analysis by PEAKS
Published datasets [1,2] were used as examples to demonstrate the capability of SILAC-based data analysis (PTM profiling) in PEAKS Studio.
Case Study: Background & Aim
Casein Kinase 2 (CSNK2) has been shown to be upregulated in many cancers, wherein its elevated expression has been linked to poor prognosis. This has deemed CSNK2 a potential target for anti-cancer therapy.
Gyenis and his team [1] devised an approach for the large-scale identification and validation of CSNK2 substrates, using an inhibitor-resistant mutant kinase to clarify differential phosphorylation resulting from on- versus off-target effects of inhibitors. The mutant kinase remains active in the presence of the inhibitor and therefore, bona fide sites remain phosphorylated when compared with the inhibitor-sensitive wild-type kinase. Phosphosites which are downregulated due to off-target effects remain downregulated in cells expressing the inhibitor-resistant mutant.
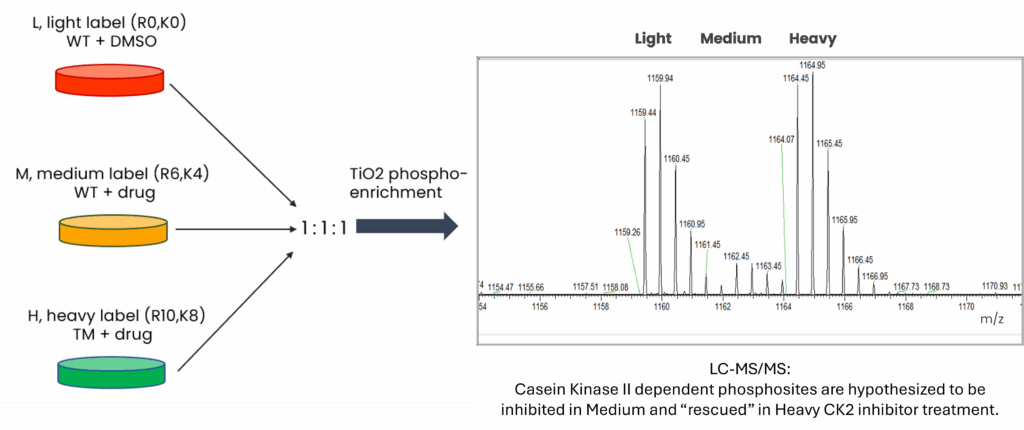
Experimental Design
Inhibition and rescue of CSNK2-dependent phosphorylation was demonstrated using Flp-In T-REx U2OS cell lines stably expressing CSNK2A-HA WT or CSNK2A-HA TM with tight Tetracycline (Tet-ON) regulation [2]. CSNK2A-HA TM was assigned a Heavy label was a chemically altered cell line expressing a triple mutant CK2A1, which has certain residues substituted to resist inhibitor drug binding and keep the catalytic activity.
Inhibitor efficacy and specificity of two inhibitor drugs, CX-4945 or SGC-CK2-1, at three time points (0 hours, 4 hours, and 24 hours) was assessed using a triple SILAC phosphoproteomic strategy:
- Control – CSNK2A-HA WT was assigned a Light label for DMSO control,
- Inhibition – CSNK2A-HA WT was assigned a Medium label (K4, R6) and treated with the inhibitor drug,
- Rescue – CSNK2A-HA TM was assigned a Heavy label (K8, R10) and treated with the inhibitor drug.
Result & Conclusion
PEAKS was used for sensitive identification of phosphorylated peptides and proteins followed by accurate quantification using a built-in triple SILAC method. Here, we demonstrated a comparison of efficacy of the two CSNK2 inhibitor drugs, CX-4945 and SGC-CK2-1, where the later appeared to be a significantly more selective inhibitor of CSNK2 as reported in the publication. The majority of SGC-CK2-1-induced decrease in phosphorylation was rescued with CSNK2A1-TM and thus determined to be entirely CSNK2A1-dependent. PEAKS was shown to clearly capture the profiles of Light, Medium, and Heavy conditions as hypothesized. This in turn allowed for a comprehensive investigation and validation of the CSNK2 dependent Inhibition (Medium) and Rescue (Heavy) at 4- and 24-hours treatment time points.
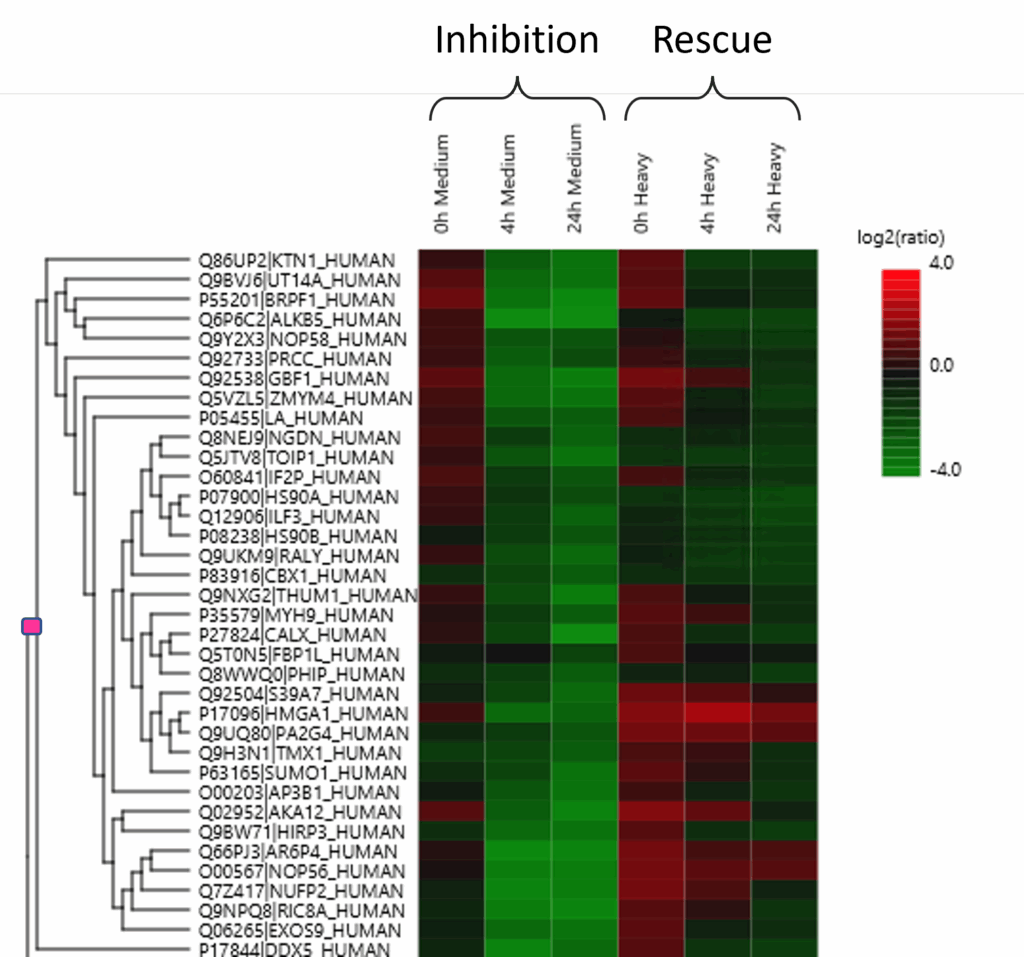
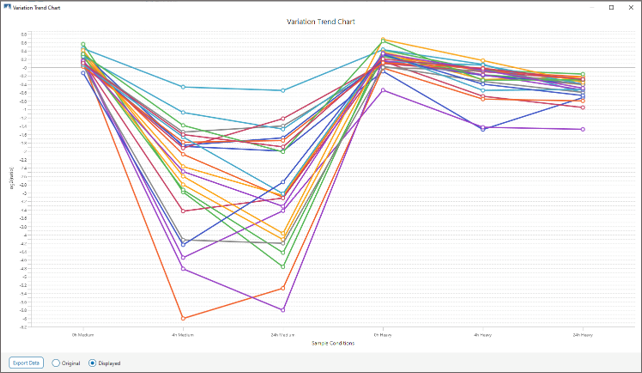
Enriched Phosphoproteome Heat map and Profiling Changes.
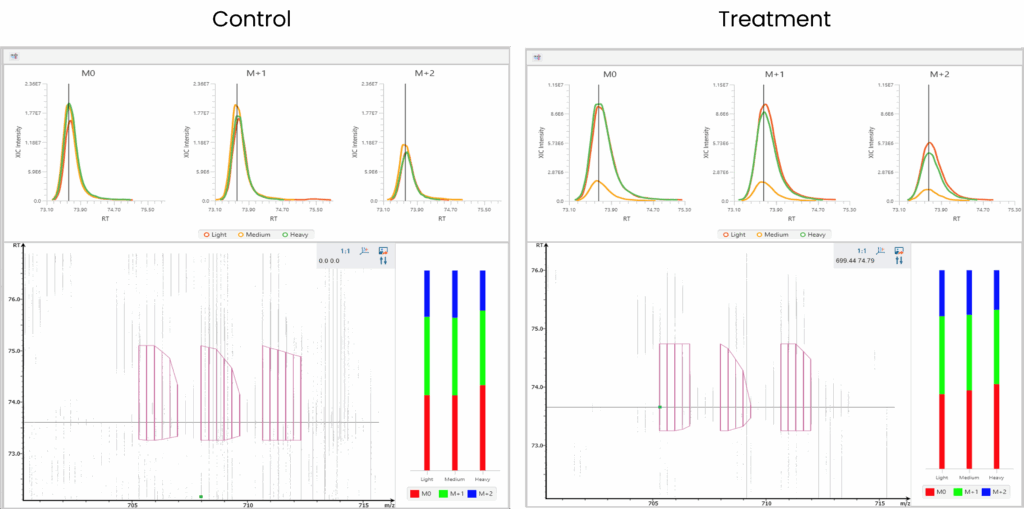
Demonstration of CSNK2 dependent phosphorylation via inhibition (Medium label, WT) and rescue (Heavy label, TM).
In conclusion, PEAKS is suitable for analysis of complex SILAC based quantification approaches and was shown successful in identifying and validating of bona fide CSNK2A1 substrates using a built-in triple SILAC based workflow.
References
- Gyenis L, Menyhart D, Cruise ES, Jurcic K, Roffey SE, Chai DB, Trifoi F, Fess SR, Desormeaux PJ, Núñez de Villavicencio Díaz T, Rabalski AJ, Zukowski SA, Turowec JP, Pittock P, Lajoie G, Litchfield DW. Chemical Genetic Validation of CSNK2 Substrates Using an Inhibitor-Resistant Mutant in Combination with Triple SILAC Quantitative Phosphoproteomics. Front Mol Biosci. 2022 doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.909711.
- Menyhart D, Gyenis L, Jurcic K, Roffey SE, Puri A, Jovanovic P, Szkop KJ, Pittock P, Lajoie G, Axtman AD, Larsson O, Topisirovic I, Litchfield DW. Comparison of CX-4945 and SGC-CK2-1 as inhibitors of CSNK2 using quantitative phosphoproteomics: Triple SILAC in combination with inhibitor-resistant CSNK2. Current Res in Chem Biology. 2023 doi: 10.1016/j.crchbi.2023.100041.

