

PEAKS is well-known and considered the gold standard for peptide de novo sequencing. To advance de novo sequencing even further, BSI was first to introduce deep learning technology into peptide de novo sequencing of mass spectrometry data and reported a significant improvement in accuracy [1,2]. The speed and accuracy of this technology naturally draws interest to integrate our solution, DeepNovo, into PEAKS.
As a key technology for finding novel peptides from mass spectrometry (MS) data, DeepNovo provides an advanced solution and will push research like antibody sequencing and neoantigen discovery further.
Key Features
- Enhanced DeepNovo – Integrated with GraphNovo, a graph-based deep learning de novo sequencing to increase amino acid and peptide level accuracy
- Harness GPUs and accelerate de novo sequencing
- Unbiased FDR control for evaluating peptide sequencing
- Improvements of next level deep learning based DeepNovo peptide sequencing observed across different sample types
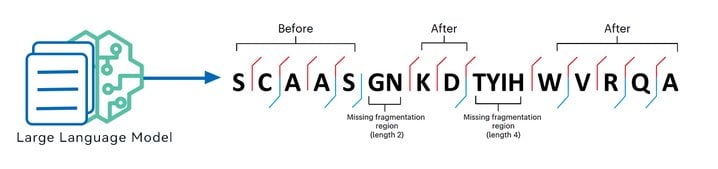
Empowered by the latest GraphNovo algorithm, the new DeepNovo sequencing algorithm resolved the issue of accumulated prediction errors due to missing fragment ions by finding the optimal path in the first stage to guide sequence prediction in the second stage.
FDR control for Peptide Sequencing
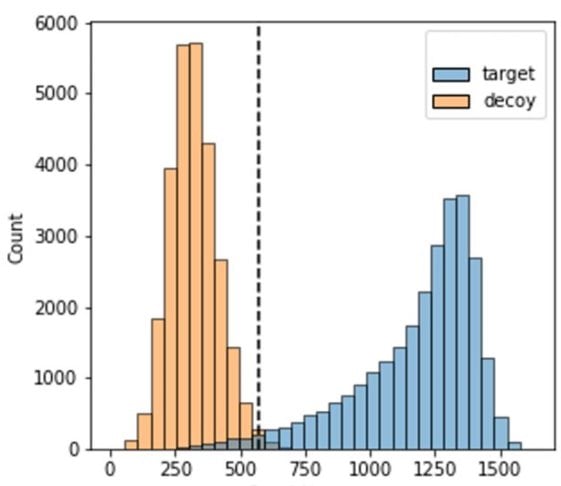
PEAKS 12 implemented a new unbiased approach to evaluate de novo peptide sequencing methods using a target-decoy spectra to estimate their FDRs. Decoy MS2 spectra were created from target MS2 spectra by keeping the numbers of peaks between decoy and target MS2 spectra similar as well as by ensuring a very similar m/z and intensity distributions of target and decoy peaks. In addition to conventional filtering based on % ALC (Average Local Confidence) Score, an FDR curve of de novo sequencing is now available in DeepNovo.
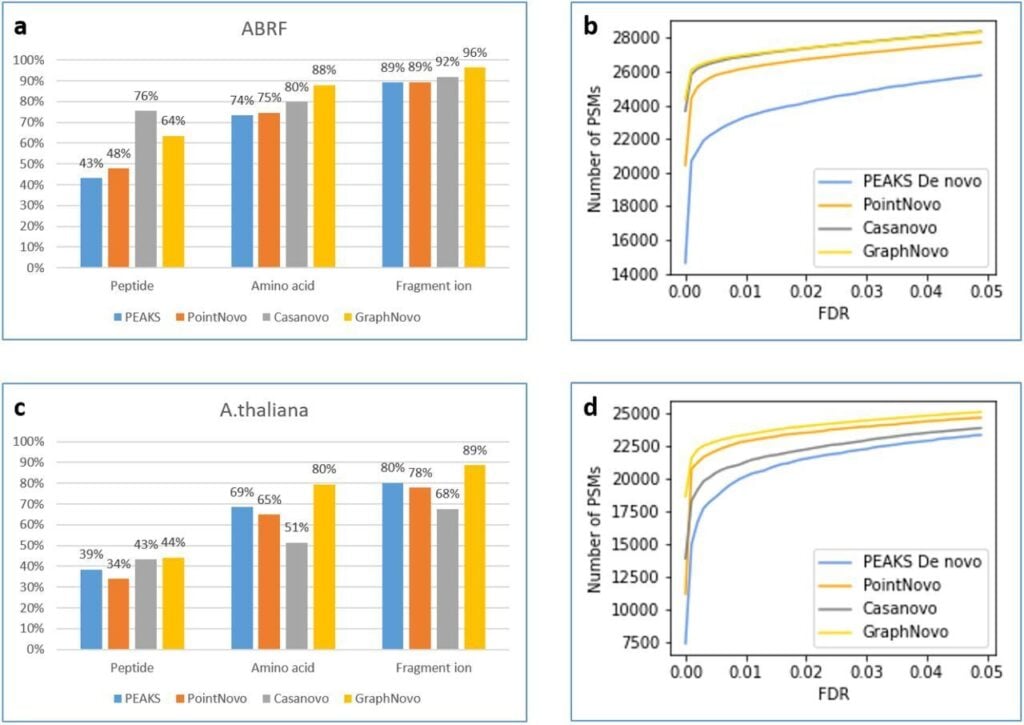
Next level DeepNovo sequencing with improved accuracy and sensitivity.
PEAKS 12 latest GraphNovo sequencing algorithm as compared to the traditional PEAKS Denovo sequencing algorithm as well as to deep learning based PointNovo and Casanovo algorithms using raw data originating from different sources, including human and HLA samples.
For human dataset, at 1% FDR cutoff, PEAKS, PointNovo, Casanovo, and Graphnovo reported 23,300, 26,194, 26,892, and 26,982 target de novo PSMs, respectively. Graphnovo also performed the best at 63%, 85%, and 96% accuracy at the peptide, amino acid, and fragment ion levels respectively.
Similar result was obtained for HLA datasets, which makes PEAKS 12 next level DeepNovo sequencing key to novel peptide discovery and immunopeptidome analysis.
References & Resources
References
- Tran, N. H., et al. (2017). De novo peptide sequencing by deep learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(31), 8247–8252. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705691114
- Tran, N. H., et al. (2019). Deep learning enables de novo peptide sequencing from data-independent-acquisition mass spectrometry. Nature methods, 16(1), 63–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-018-0260-3
- Mao, Z., et al. (2023). Mitigating the missing-fragmentation problem in de novo peptide sequencing with a two-stage graph-based deep learning model. Nature Machine Intelligence (5) 1250–1260. doi.org/10.1038/s42256-023-00738-x
- Tran, N. H., et al. (2024). NovoBoard: a comprehensive framework for evaluating the false discovery rate and accuracy of de novo peptide sequencing. bioRxiv. 589668. doi:10.1101/2024.04.16.589668

